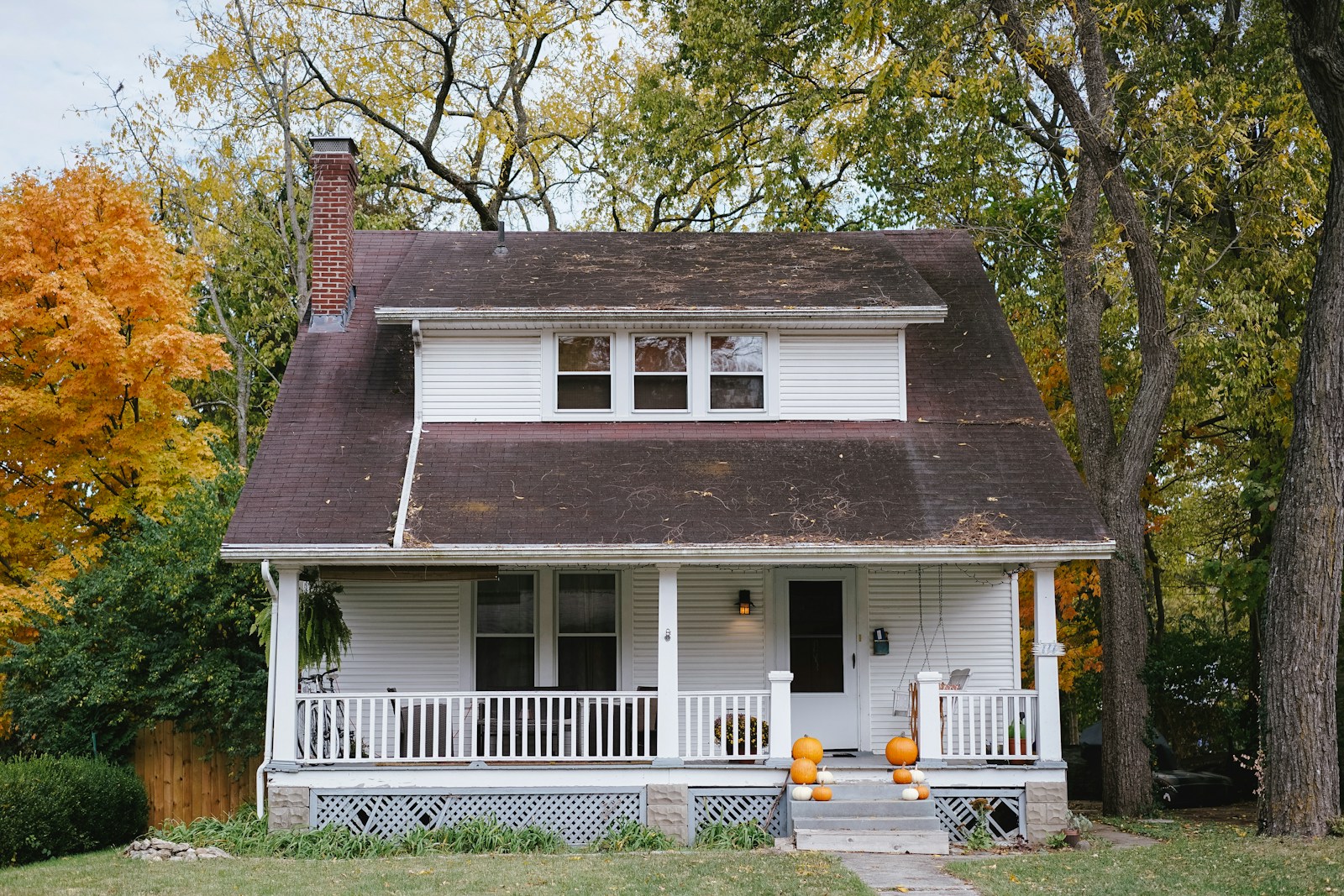
The exterior inspection of a property is a critical first step in assessing its overall condition and identifying potential issues that may not be immediately visible. This phase involves a thorough examination of the building’s façade, foundation, and surrounding landscape. Inspectors typically begin by evaluating the condition of the siding, whether it be wood, vinyl, brick, or stucco.
Signs of wear, such as peeling paint, cracks, or warping, can indicate underlying problems that may require further investigation. For instance, wood siding that shows signs of rot may suggest prolonged exposure to moisture, which could lead to more significant structural issues if not addressed promptly. In addition to the siding, the foundation is scrutinized for any visible cracks or signs of settling.
A foundation that is shifting or cracking can lead to serious structural problems down the line. Inspectors often look for unevenness in the ground around the foundation, which can indicate drainage issues or soil erosion. Furthermore, the landscaping is assessed for proper grading and drainage away from the home.
Poor drainage can lead to water pooling around the foundation, increasing the risk of water intrusion and damage. The exterior inspection also includes an evaluation of windows and doors for proper sealing and functionality, as well as checking for any signs of insect infestation or decay.
Key Takeaways
- Exterior inspection should include checking for any signs of damage, such as cracks, peeling paint, or water stains.
- Interior inspection should focus on checking for any signs of water damage, mold, or pest infestation.
- Structural inspection should involve checking for any signs of foundation issues, such as cracks or uneven floors.
- Plumbing inspection should include checking for leaks, water pressure, and proper drainage.
- Electrical inspection should involve checking for any faulty wiring, outdated electrical panels, or potential fire hazards.
- HVAC inspection should focus on checking the condition of the heating and cooling systems, as well as the ventilation.
- Roof inspection should include checking for any signs of damage, such as missing shingles, leaks, or sagging areas.
- Pest and mold inspection should involve checking for any signs of infestation or mold growth, as well as any damage caused by pests.
Interior Inspection
The interior inspection focuses on the condition of the living spaces within the home. This includes a detailed examination of walls, ceilings, floors, and fixtures. Inspectors look for signs of water damage, such as stains or discoloration on ceilings and walls, which may indicate leaks from plumbing or roofing issues.
They also assess the condition of flooring materials—whether hardwood, tile, or carpet—for signs of wear and tear or damage. For example, buckling hardwood floors can suggest moisture problems beneath the surface, while stained carpets may indicate past flooding or inadequate cleaning. In addition to visual assessments, inspectors often test the functionality of various systems within the home.
This includes checking doors and windows for proper operation and ensuring that locks and latches are secure. Inspectors also evaluate the condition of kitchen and bathroom fixtures, such as sinks, faucets, and toilets. They look for leaks, corrosion, or signs of mold growth around these areas.
The interior inspection is not just about identifying current issues; it also involves assessing the overall livability and safety of the space. This includes checking for adequate ventilation and ensuring that smoke detectors and carbon monoxide detectors are present and functioning.
Structural Inspection
A structural inspection delves deeper into the integrity of a building’s framework. This phase is crucial for identifying any potential safety hazards that could arise from compromised structural elements. Inspectors examine load-bearing walls, beams, and columns to ensure they are sound and free from damage.
They look for signs of sagging or bowing in floors and ceilings, which can indicate serious structural concerns. For instance, a sagging ceiling may suggest that the roof structure is failing or that there is excessive weight being placed on it. Additionally, inspectors assess the attic and crawl spaces for signs of structural integrity.
In attics, they check for proper bracing and ventilation, as well as any signs of pest infestations that could compromise wood structures. In crawl spaces, they look for moisture issues that could lead to rot or mold growth. The inspection also includes evaluating the overall design of the structure to ensure it meets local building codes and standards.
Any deviations from these codes can pose risks not only to the building’s integrity but also to the safety of its occupants.
Plumbing Inspection
The plumbing inspection is a vital component of a comprehensive property assessment. Inspectors evaluate both the visible plumbing fixtures and the hidden systems within walls and beneath floors. They begin by checking for leaks in exposed pipes under sinks and in basements or crawl spaces.
A small leak can quickly escalate into a significant problem if left unaddressed, leading to water damage and mold growth. Inspectors also assess water pressure to ensure it meets acceptable standards; low water pressure can indicate clogs or issues within the plumbing system. In addition to visible components, inspectors often evaluate the age and condition of major plumbing systems such as water heaters and sewer lines.
For example, older water heaters may be nearing the end of their lifespan and could require replacement soon. Inspectors may also conduct tests on drainage systems to ensure they are functioning properly; slow drains can signal blockages that need immediate attention. Furthermore, they check for proper venting of plumbing systems to prevent sewer gases from entering living spaces.
A thorough plumbing inspection not only identifies current issues but also helps homeowners anticipate future repairs.
Electrical Inspection
An electrical inspection is essential for ensuring the safety and functionality of a home’s electrical system. Inspectors begin by examining the main electrical panel for signs of wear or improper installation. They check for adequate grounding and bonding, which are crucial for preventing electrical shocks and fires.
Additionally, inspectors assess circuit breakers to ensure they are functioning correctly and are appropriately rated for the circuits they protect. Beyond the main panel, inspectors evaluate wiring throughout the home. They look for outdated wiring types such as knob-and-tube or aluminum wiring, which can pose safety hazards due to their susceptibility to overheating and failure.
Inspectors also check outlets and switches for proper operation and grounding; any loose connections can lead to arcing and potential fire risks. Furthermore, they assess lighting fixtures for proper installation and functionality.
A comprehensive electrical inspection not only identifies existing problems but also helps homeowners understand their system’s capacity to handle modern electrical demands.
HVAC Inspection
The HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) inspection is crucial for ensuring a comfortable living environment year-round. Inspectors begin by evaluating the heating system, whether it be a furnace or heat pump. They check for proper operation, including airflow and temperature consistency throughout the home.
Inspectors also examine ductwork for leaks or blockages that could hinder efficiency. In addition to heating systems, inspectors assess air conditioning units for functionality and efficiency. They check refrigerant levels and inspect coils for cleanliness; dirty coils can significantly reduce efficiency and increase energy costs.
The ventilation system is also evaluated to ensure adequate airflow throughout living spaces. Inspectors look for signs of mold growth in ducts or around vents, which can impact indoor air quality. A thorough HVAC inspection not only identifies current issues but also provides insights into maintenance needs that can prolong system life.
Roof Inspection
A roof inspection is a critical aspect of property assessment that can prevent costly repairs down the line. Inspectors begin by examining shingles or roofing materials for signs of wear or damage. This includes looking for missing shingles, curling edges, or granule loss on asphalt shingles that can indicate aging or deterioration.
Inspectors also assess flashing around chimneys and vents to ensure they are watertight; improper flashing can lead to leaks that compromise both roofing materials and interior spaces. In addition to visible assessments from ground level, inspectors often utilize ladders or drones to get a closer look at hard-to-reach areas. They check gutters and downspouts for blockages that could lead to water pooling on the roof surface or around the foundation.
Inspectors also evaluate the overall slope of the roof to ensure proper drainage away from the home. A well-maintained roof is essential not only for protecting a home from weather elements but also for maintaining its overall structural integrity.
Pest and Mold Inspection
The final phase of a comprehensive property inspection involves assessing for pests and mold—two issues that can significantly impact both health and property value.
Inspectors look for signs of pest infestations such as droppings, nests, or damage to wood structures caused by termites or carpenter ants.
They often check basements, attics, and crawl spaces where pests are likely to hide or enter a home.
Mold inspections are equally important due to their potential health risks. Inspectors look for visible mold growth in damp areas such as bathrooms or basements but also utilize moisture meters to detect hidden mold behind walls or under flooring materials. They assess ventilation systems to ensure they are not contributing to moisture buildup that fosters mold growth.
A thorough pest and mold inspection provides homeowners with critical information about potential health hazards and necessary remediation steps to maintain a safe living environment. In summary, each phase of property inspection plays a vital role in assessing a home’s condition comprehensively. From exterior evaluations to detailed assessments of plumbing, electrical systems, HVAC units, roofs, pests, and mold—each aspect contributes to understanding a property’s overall health and safety.
FAQs
What is a home inspection?
A home inspection is a thorough examination of the condition of a property, typically performed before the sale of a home. It is conducted by a professional home inspector to identify any issues or potential problems with the property.
Why is a home inspection important?
A home inspection is important because it can uncover any hidden issues with the property that may not be apparent to the buyer. It can also provide peace of mind and help the buyer make an informed decision about the purchase.
What are some common things to look for during a home inspection?
During a home inspection, it is important to look for issues such as structural problems, electrical and plumbing issues, water damage, mold, pest infestations, and the condition of the roof, HVAC system, and appliances.
Who typically pays for a home inspection?
In most cases, the buyer is responsible for paying for the home inspection. However, it is ultimately up to the parties involved in the real estate transaction to determine who will cover the cost.
How long does a home inspection typically take?
The duration of a home inspection can vary depending on the size and condition of the property. On average, a home inspection can take anywhere from 2 to 4 hours to complete.
Can a home inspection uncover all potential issues with a property?
While a home inspection can uncover many issues with a property, it is not guaranteed to uncover every potential problem. Some issues may be hidden or not readily apparent at the time of the inspection.